Gfci breaker for old two wire – GFCI breakers for old two-wire systems offer a crucial layer of protection against electrical hazards, safeguarding your home and loved ones. Dive into this comprehensive guide to understand their purpose, benefits, installation process, and maintenance tips, empowering you to make informed decisions about electrical safety in your home.
As we delve into the world of electrical safety, we’ll explore the different types of GFCI breakers available for old two-wire systems, their features, and how to choose the best one for your specific needs.
Overview of GFCI Breakers for Old Two-Wire Systems
In older homes with two-wire electrical systems, the lack of a grounding wire poses a safety hazard. GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) breakers address this issue by continuously monitoring the electrical current flowing through a circuit. If an imbalance is detected, indicating a ground fault, the GFCI breaker swiftly trips, cutting off power to prevent electrical shock.
Safety Benefits of GFCI Breakers in Old Two-Wire Systems
GFCI breakers offer significant safety advantages in old two-wire systems:
- Protection from Electrical Shock:GFCI breakers prevent serious injuries or fatalities by tripping the circuit when even a small amount of current leaks to the ground, minimizing the risk of electrocution.
- Enhanced Safety in Wet Areas:Bathrooms, kitchens, and other areas with water sources are prone to electrical hazards. GFCI breakers provide an added layer of protection in these locations, preventing shocks from faulty appliances or accidental water contact.
- Compliance with Electrical Codes:Many electrical codes now require GFCI protection in certain areas of homes and businesses, ensuring compliance and enhancing overall electrical safety.
Types of GFCI Breakers for Old Two-Wire Systems
GFCI breakers for old two-wire systems come in different types, each with its own features and benefits. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right breaker for your specific needs.
Plug-On GFCI Breakers
Plug-on GFCI breakers are a convenient and cost-effective option for adding GFCI protection to existing two-wire circuits. These breakers simply plug onto the existing breaker panel, eliminating the need for rewiring. They are available in both standard and tamper-resistant versions.
Circuit Breaker GFCI Breakers
Circuit breaker GFCI breakers are a more permanent solution for adding GFCI protection. They replace the existing circuit breaker in the panel and provide GFCI protection for the entire circuit. These breakers are more expensive than plug-on breakers, but they offer a more reliable and permanent solution.
Installing a GFCI breaker for an old two-wire system is a task that requires caution. But if you’re feeling sleepy while tackling this project, you might want to check out the get some sleep crossword clue . After catching some Z’s, you’ll be refreshed and ready to finish wiring that GFCI breaker like a pro.
Receptacle GFCI Breakers
Receptacle GFCI breakers combine the functions of a GFCI outlet and a circuit breaker into a single device. They are installed in place of a standard outlet and provide GFCI protection for the entire circuit. Receptacle GFCI breakers are a good option for adding GFCI protection to outlets in areas where it is difficult or impossible to install a GFCI outlet, such as in crawl spaces or attics.
Installation of GFCI Breakers for Old Two-Wire Systems
Installing GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems requires careful attention to safety and proper wiring techniques. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Safety Precautions
* Turn off the main power supply to the electrical panel before starting any work.
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and safety glasses.
- Ensure that the work area is well-lit and free of clutter.
Wiring Diagrams, Gfci breaker for old two wire
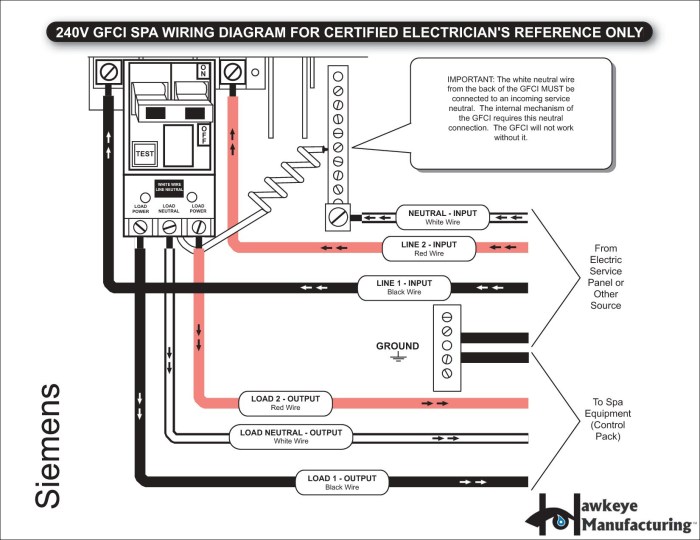
Refer to the wiring diagrams provided by the GFCI breaker manufacturer for specific instructions on how to connect the wires. Typically, the black wire (hot) connects to the LINE terminal, and the white wire (neutral) connects to the LOAD terminal.
Step-by-Step Installation
1.
-
-*Remove the Existing Breaker
Turn off the circuit breaker that controls the two-wire system. Remove the faceplate and unscrew the existing breaker. Pull it out of the panel.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
-*Connect the GFCI Breaker
Connect the black wire to the LINE terminal and the white wire to the LOAD terminal on the GFCI breaker. Tighten the screws securely.
-*Install the GFCI Breaker
Slide the GFCI breaker into the panel and secure it with the screws.
-*Turn on the Power
Turn on the main power supply and the circuit breaker that controls the two-wire system.
-*Test the GFCI Breaker
Press the “TEST” button on the GFCI breaker. It should trip and cut off power to the circuit. Press the “RESET” button to restore power.
Additional Tips
* If the GFCI breaker trips frequently, it may indicate a ground fault in the wiring. Consult a qualified electrician to identify and fix the issue.
- GFCI breakers should be installed in areas where water or moisture is present, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets.
- Regularly test GFCI breakers to ensure they are functioning properly.
Troubleshooting GFCI Breakers for Old Two-Wire Systems
GFCI breakers, while effective in preventing electrical accidents, can sometimes encounter issues in old two-wire systems. Understanding these common problems and their solutions can help ensure the proper functioning and safety of your electrical system.
One common issue is the tripping of the GFCI breaker without any apparent fault. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Loose or damaged wiring
- Ground faults in the system
- Overloading of the circuit
- Malfunctioning GFCI breaker
To troubleshoot these issues, first check the wiring for any loose connections or damage. If the wiring appears to be in good condition, reset the GFCI breaker and observe if it trips again. If it does, there may be a ground fault in the system.
To locate the fault, use a voltage tester to check for voltage between the neutral and ground wires. If there is voltage present, there is a ground fault that needs to be repaired.
If the GFCI breaker trips due to overloading, reduce the load on the circuit by unplugging unnecessary appliances or devices. If the breaker continues to trip, there may be a problem with the breaker itself. Replace the breaker with a new one of the same type and amperage rating.
In some cases, the GFCI breaker may malfunction and need to be replaced. If you have checked all the other potential causes and the breaker is still tripping, it is likely faulty and should be replaced.
Remember, working with electricity can be dangerous. If you are not comfortable troubleshooting electrical issues, it is best to contact a qualified electrician for assistance.
Maintenance of GFCI Breakers for Old Two-Wire Systems
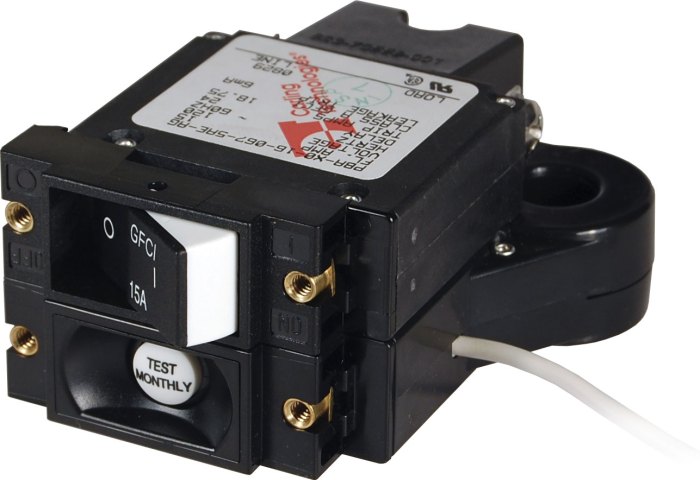

Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and safety of GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems. Neglecting maintenance can compromise the breaker’s ability to protect against electrical hazards, potentially leading to serious accidents.
Recommended Maintenance Procedures and Schedules
The following maintenance procedures and schedules are recommended for GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems:
- Monthly Visual Inspection:Visually inspect the breaker for any physical damage, such as cracks, dents, or discoloration. Also, check the wiring connections to ensure they are secure.
- Quarterly Functional Testing:Perform a functional test on the breaker by pressing the “Test” button. The breaker should trip and reset immediately, indicating proper operation.
- Annual Comprehensive Inspection:Hire a qualified electrician to perform a comprehensive inspection of the breaker and its wiring. This inspection should include testing the breaker’s sensitivity, response time, and ground fault detection capabilities.
By adhering to these maintenance procedures and schedules, homeowners can ensure the continued reliability and safety of their GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems.
Benefits of Using GFCI Breakers in Old Two-Wire Systems
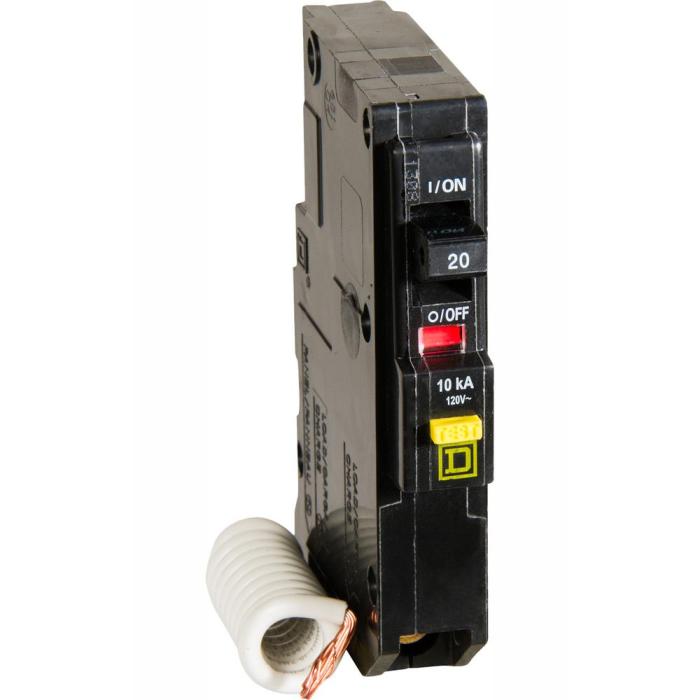

Integrating GFCI breakers into old two-wire systems offers significant advantages that enhance electrical safety and protect against potential hazards.
One crucial benefit lies in their ability to prevent electrical shock, a leading cause of injuries and fatalities in electrical accidents. GFCI breakers monitor electrical current flow and swiftly disconnect the circuit if an imbalance is detected, such as when current leaks through a person’s body.
This rapid response minimizes the risk of severe electrical shocks, reducing the likelihood of serious injuries or death.
Enhanced Ground Fault Protection
In old two-wire systems, grounding is often inadequate or absent, making them vulnerable to ground faults. GFCI breakers address this issue by continuously monitoring the current flowing through the circuit and comparing it to the current returning. If a discrepancy is detected, indicating a ground fault, the breaker promptly interrupts the circuit, preventing potentially dangerous situations.
Reduced Risk of Electrical Fires
Electrical fires can result from various factors, including overloads and ground faults. GFCI breakers play a vital role in mitigating these risks by swiftly disconnecting the circuit when an abnormal current flow is detected. This rapid response prevents overheating and the potential ignition of electrical components, significantly reducing the likelihood of electrical fires.
Limitations of GFCI Breakers for Old Two-Wire Systems
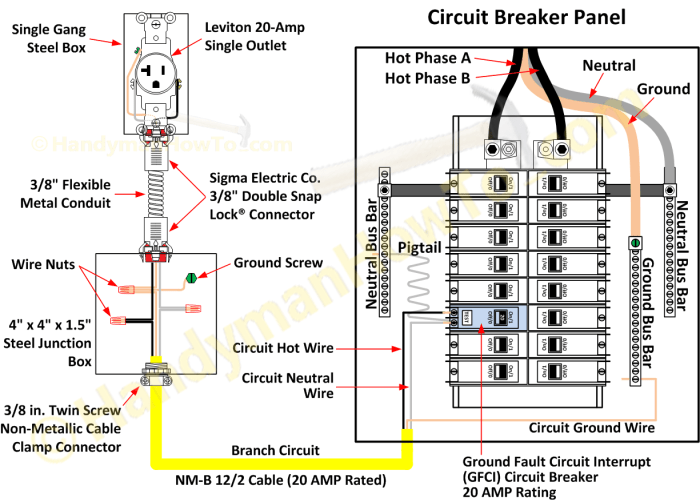
While GFCI breakers provide significant safety benefits, they have certain limitations in old two-wire systems:
One limitation is that GFCI breakers require a grounded neutral wire. In old two-wire systems, the neutral wire may not be grounded, which can prevent the GFCI breaker from functioning properly.
Mitigation:
To mitigate this, a grounding electrode, such as a ground rod or cold water pipe, can be installed to provide a ground path for the neutral wire.
Another limitation is that GFCI breakers can be more sensitive than traditional circuit breakers, which may lead to nuisance tripping. This can be particularly problematic in older homes with appliances that draw high currents, such as air conditioners or refrigerators.
Mitigation:
To minimize nuisance tripping, choose a GFCI breaker with a higher amperage rating or consider installing a dedicated circuit for high-current appliances.
Additionally, old two-wire systems may have deteriorated wiring or connections, which can affect the performance of GFCI breakers. It is important to have the electrical system inspected by a qualified electrician to ensure that it is in good condition before installing GFCI breakers.
Safety Considerations for Using GFCI Breakers in Old Two-Wire Systems: Gfci Breaker For Old Two Wire
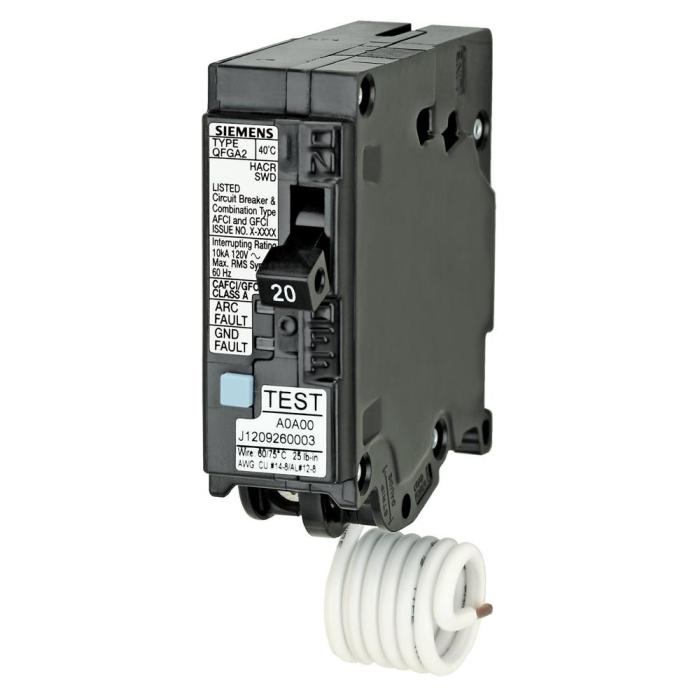

Electrical safety is paramount when working with GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems. Neglecting safety guidelines can lead to electrical shocks, fires, and severe injuries. Adhering to the following guidelines is crucial to ensure a safe working environment.
Electrical Safety Guidelines
- Always turn off the power at the main breaker or fuse box before working on any electrical components.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as rubber gloves and safety glasses.
- Use a non-contact voltage tester to confirm that the power is off before touching any wires.
- Never work on live electrical circuits.
- If you are not comfortable working with electricity, hire a qualified electrician to perform the installation or repairs.
Grounding Requirements
Proper grounding is essential for the safe operation of GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems. The grounding wire provides a path for excess electrical current to flow safely into the ground, preventing it from traveling through the body in the event of a fault.
In old two-wire systems, grounding may not be present or may be inadequate. It is crucial to ensure that a proper grounding system is installed before using GFCI breakers. This may involve running a grounding wire from the electrical panel to a grounding rod or other suitable grounding point.
Testing and Maintenance
Regular testing and maintenance are crucial to ensure that GFCI breakers are functioning correctly and providing adequate protection. GFCI breakers should be tested monthly by pressing the “Test” button. If the breaker does not trip, it should be replaced immediately.
Additionally, GFCI breakers should be inspected periodically for any signs of damage or wear. If any damage is detected, the breaker should be replaced.
Code Requirements for GFCI Breakers in Old Two-Wire Systems
Electrical codes establish guidelines for the safe installation and use of GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems to minimize electrical hazards and ensure occupant safety.
These code requirements are based on the principle that GFCI breakers provide an additional layer of protection against electrical shocks by detecting imbalances in current flow and tripping the circuit to prevent serious injury or electrocution.
Reasons for Code Requirements
- Protection against Electrical Shocks: GFCI breakers are designed to trip quickly when they detect an imbalance in current flow, preventing the flow of harmful electrical currents through the body.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Electrical codes incorporate the latest safety standards and best practices, and requiring GFCI breakers in old two-wire systems ensures compliance with these standards.
- Prevention of Electrical Fires: Electrical shocks can cause fires, and GFCI breakers help prevent these fires by quickly interrupting the flow of electricity in the event of a fault.
- Protection of Sensitive Electronics: Old two-wire systems may not provide adequate protection for sensitive electronic devices, and GFCI breakers help protect these devices from damage caused by electrical surges or faults.
Comparison of GFCI Breakers to Other Safety Devices for Old Two-Wire Systems
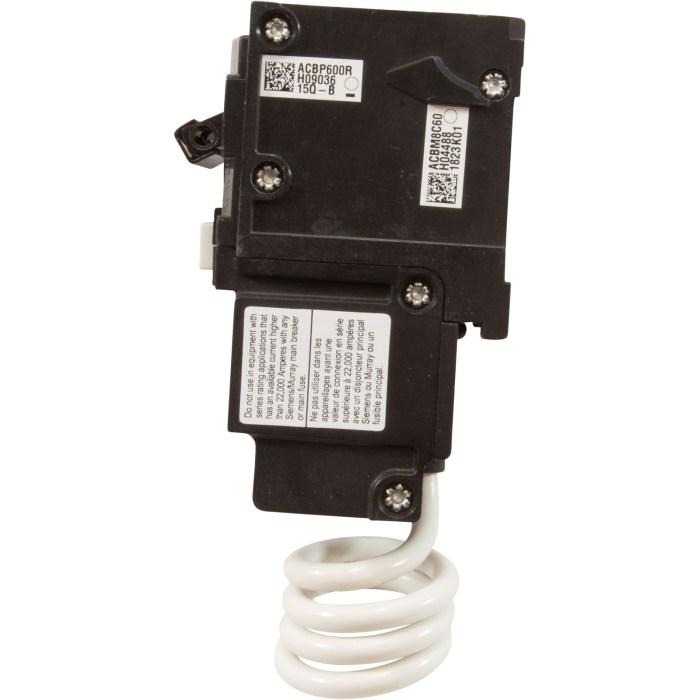

GFCI breakers are not the only safety devices available for old two-wire systems. Other options include fuses and surge protectors. Each device has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the right one for your specific application.
Fuses are the most basic type of safety device. They simply break the circuit when the current flow exceeds a certain level. This can help to prevent fires, but it does not provide any protection against electrical shocks. Surge protectors, on the other hand, are designed to protect against voltage spikes.
These spikes can damage electronic equipment, but they are not a major hazard to humans.
GFCI breakers offer the best protection against both electrical shocks and fires. They are more expensive than fuses or surge protectors, but they are worth the investment if you are concerned about safety.
Advantages of GFCI Breakers
- Provide protection against both electrical shocks and fires
- Easy to install
- Require no maintenance
Disadvantages of GFCI Breakers
- More expensive than fuses or surge protectors
- Can trip nuisancely
Recommendations
- Use GFCI breakers in all new installations
- Replace old fuses with GFCI breakers as they fail
- Install surge protectors on all electronic equipment
Answers to Common Questions
What is the primary function of a GFCI breaker?
GFCI breakers monitor electrical current flow and quickly interrupt the circuit if an imbalance is detected, preventing potentially dangerous shocks.
Why are GFCI breakers particularly important for old two-wire systems?
Old two-wire systems often lack proper grounding, making them more susceptible to electrical faults and shocks. GFCI breakers compensate for this lack of grounding, providing an additional layer of protection.
How often should GFCI breakers be tested?
It’s recommended to test GFCI breakers monthly by pressing the “Test” button. This ensures they are functioning correctly and will trip when necessary.