Neuron structure worksheet answers pogil – Unveiling the intricacies of neuron structure, this comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental components and specialized functions of these essential building blocks of the nervous system. Prepare to embark on an exploration of neuronal anatomy, unraveling the secrets of how neurons communicate, process information, and shape our cognitive abilities.
1. Neuron Structure Overview
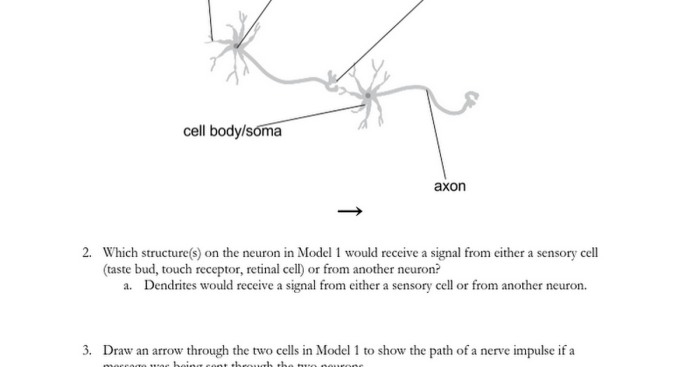
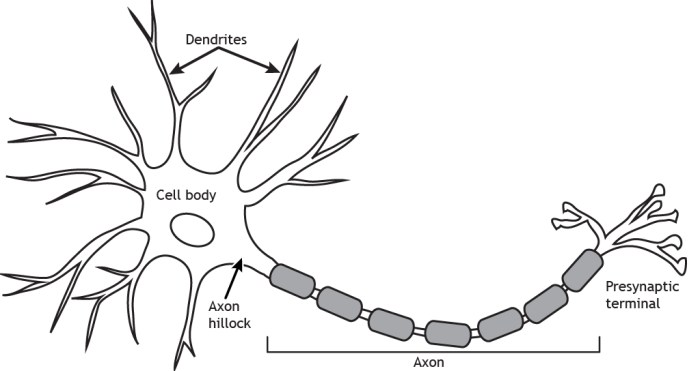
Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system. They are specialized cells that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. The basic structure of a neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon.
The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles responsible for the neuron’s metabolic functions. Dendrites are short, branched extensions of the cell body that receive signals from other neurons. The axon is a long, thin extension of the cell body that transmits signals to other neurons or muscles.
There are different types of neurons, each with a specialized function. Sensory neurons transmit sensory information from the body to the brain. Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain to muscles. Interneurons connect neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
The following table summarizes the key structural features of neurons:
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell body (soma) | Contains the nucleus and other organelles responsible for the neuron’s metabolic functions |
| Dendrites | Receive signals from other neurons |
| Axon | Transmits signals to other neurons or muscles |
2. Cell Body and Dendrites
The cell body (soma) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus, which houses the neuron’s DNA. The cell body also contains other organelles responsible for the neuron’s metabolic functions, such as the mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Dendrites are short, branched extensions of the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons through synapses, which are specialized junctions between neurons. The shape and structure of dendrites can influence the neuron’s function. For example, neurons with highly branched dendrites can receive signals from a wider range of other neurons.
3. Axon and Myelin Sheath
The axon is a long, thin extension of the cell body. It transmits signals to other neurons or muscles. The axon is covered by a myelin sheath, which is a layer of insulating material that speeds up signal transmission.
Myelination is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Demyelination, the loss of the myelin sheath, can lead to a variety of neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis.
4. Synapse and Neurotransmission
The synapse is the junction between two neurons. It is where signals are transmitted from one neuron to another. The synapse consists of a presynaptic neuron, a postsynaptic neuron, and a synaptic cleft.
When an electrical signal reaches the end of the axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers. Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing an electrical signal to be generated in the postsynaptic neuron.
5. Neuron Communication
Neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. Electrical signals are generated by the movement of ions across the neuron’s membrane. Chemical signals are generated by the release of neurotransmitters.
The strength of the signal that a neuron receives depends on the number of neurotransmitters that are released and the sensitivity of the receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
Neurons can also communicate with each other through synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of synapses to change their strength over time. Synaptic plasticity is essential for learning and memory.
6. Neuron Function in Nervous System
Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system. They are responsible for transmitting information throughout the body, allowing us to perceive the world around us, control our movements, and think.
Neuron dysfunction can lead to a variety of neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy.
Commonly Asked Questions: Neuron Structure Worksheet Answers Pogil
What are the main components of a neuron?
The main components of a neuron include the cell body (soma), dendrites, axon, and myelin sheath.
How do neurons communicate with each other?
Neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals at specialized junctions called synapses.
What is the role of the myelin sheath?
The myelin sheath insulates the axon and speeds up the transmission of electrical signals.