The prodromal syndrome consists of all the following except, encompassing a range of symptoms that precede the onset of a full-blown disorder or condition. Understanding the prodromal syndrome’s unique characteristics and exclusions is crucial for early identification and effective management.
This syndrome manifests as a constellation of physical, psychological, and cognitive symptoms, signaling the potential development of various mental health conditions. However, it is essential to recognize the exceptions to this definition, as certain symptoms or presentations may not fall within the prodromal syndrome’s parameters.
Prodromal Syndrome Definition
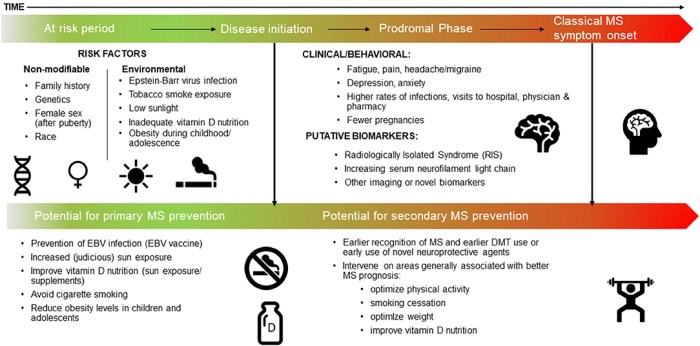
The prodromal syndrome refers to a cluster of early symptoms that often precede the onset of a full-blown disorder or condition. These symptoms may be physical, psychological, or cognitive and can vary in severity and duration.
Prodromal Syndrome Exclusions
The prodromal syndrome excludes symptoms that are:
- Specific to a particular disorder or condition
- Caused by an acute illness or injury
- Part of a normal developmental process
Prodromal Syndrome Symptoms
Prodromal symptoms can be categorized into the following domains:
Physical Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Muscle aches
- Gastrointestinal distress
- Sleep disturbances
Psychological Symptoms
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Social withdrawal
Cognitive Symptoms, The prodromal syndrome consists of all the following except
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Impaired judgment
- Slowed thinking
- Confusion
Prodromal Syndrome Duration

The duration of the prodromal syndrome can vary depending on the underlying condition. In some cases, it may last for a few days or weeks, while in others it can persist for months or even years.
Prodromal Syndrome Progression

The prodromal syndrome can progress to a full-blown disorder or condition if left untreated. This progression is often gradual and may involve the emergence of additional symptoms or an increase in the severity of existing symptoms.
Prodromal Syndrome Management
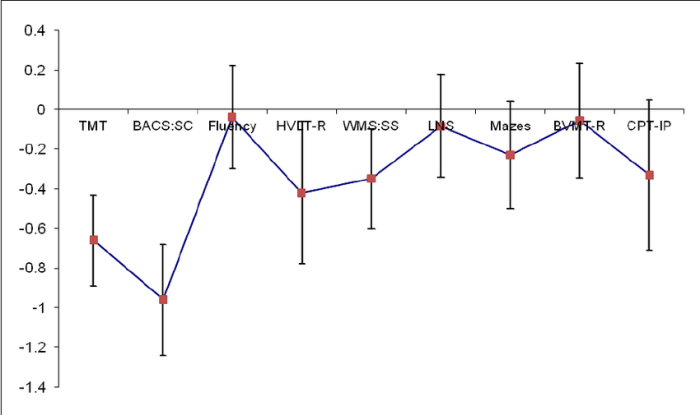
Early intervention is crucial in managing the prodromal syndrome. Strategies may include:
- Psychotherapy
- Medication
- Lifestyle changes (e.g., exercise, healthy diet, sleep hygiene)
By addressing the prodromal symptoms early on, it is possible to prevent or delay the onset of a more severe disorder or condition.
Expert Answers: The Prodromal Syndrome Consists Of All The Following Except
What are the common exclusions to the prodromal syndrome?
Exclusions may include symptoms that are unrelated to the underlying condition, such as those caused by substance use or medical conditions.
How long does the prodromal syndrome typically last?
The duration can vary depending on the underlying condition, but it generally ranges from a few weeks to several months.
What are the benefits of early intervention for the prodromal syndrome?
Early intervention can prevent the progression to more severe conditions, improve treatment outcomes, and enhance overall quality of life.