Chemistry worksheet wavelength frequency & energy of electromagnetic waves delves into the fundamental concepts that govern the behavior of light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. By exploring the intricate relationships between wavelength, frequency, and energy, we unlock a deeper understanding of the electromagnetic spectrum and its diverse applications in chemistry and beyond.
This comprehensive guide provides a thorough examination of the electromagnetic spectrum, from the high-energy gamma rays to the low-energy radio waves. It illuminates the interactions of electromagnetic waves with matter, revealing the mechanisms behind absorption, reflection, and transmission. Moreover, it showcases how these concepts are harnessed in various chemical applications, including spectroscopy and photochemistry.
Definition of Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy
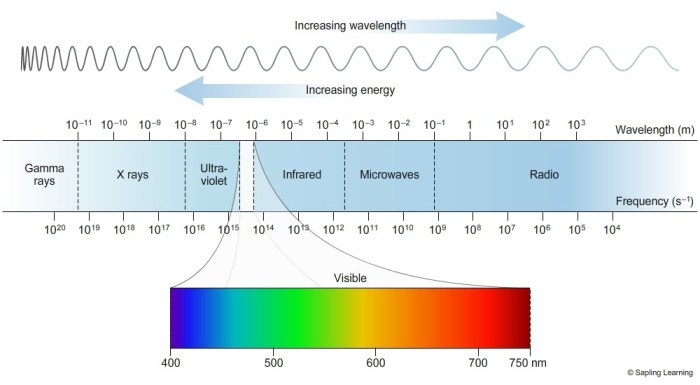
In the realm of physics, understanding the properties of electromagnetic waves requires a clear grasp of three fundamental concepts: wavelength, frequency, and energy.
Wavelength
Wavelength (λ) is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave. It is measured in meters (m) and represents the physical length of a single wave cycle.
Frequency
Frequency (ν) is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point in one second. It is measured in hertz (Hz) and represents the rate at which the wave oscillates.
Energy, Chemistry worksheet wavelength frequency & energy of electromagnetic waves
Energy (E) of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength. The relationship between these three quantities is expressed by the equation E = hν = hc/λ, where h is Planck’s constant.
Relationship between Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy
The relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy is governed by the following principles:
- Inverse Relationship between Wavelength and Frequency: As wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is inversely proportional.
- Direct Relationship between Energy and Frequency: As frequency increases, energy increases. This relationship is directly proportional.
The formula E = hν = hc/λ quantifies these relationships, where h is Planck’s constant, ν is frequency, λ is wavelength, c is the speed of light.
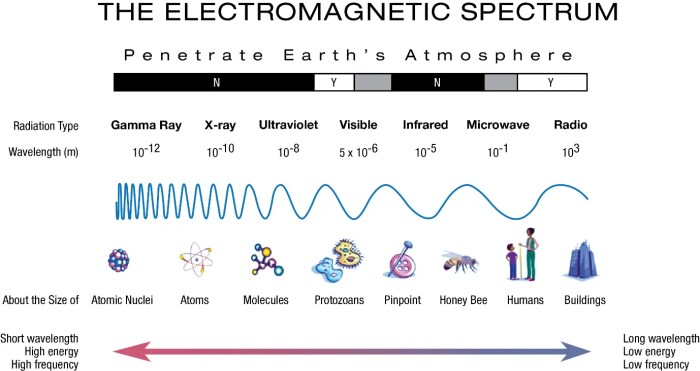
Electromagnetic Spectrum
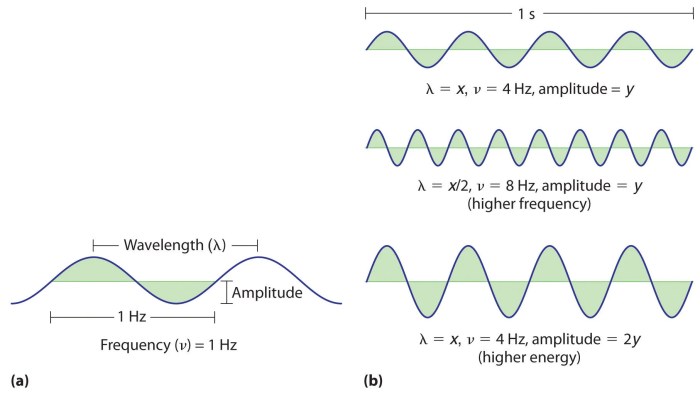
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of wavelengths and frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It encompasses all forms of electromagnetic waves, from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays.
The electromagnetic spectrum is typically divided into several regions based on wavelength and frequency, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Different types of electromagnetic waves have distinct applications in various fields, such as communication, medicine, and scientific research.
Interactions of Electromagnetic Waves with Matter
Electromagnetic waves interact with matter in various ways, including absorption, reflection, and transmission.
- Absorption: When electromagnetic waves interact with matter, they can be absorbed by the material. This process transfers energy from the wave to the material.
- Reflection: Electromagnetic waves can also be reflected by matter. This occurs when the waves bounce off a surface without being absorbed.
- Transmission: Electromagnetic waves can also be transmitted through matter. This occurs when the waves pass through the material without being absorbed or reflected.
These interactions have numerous applications in everyday life, such as communication, imaging, and medical treatments.
Applications of Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy in Chemistry: Chemistry Worksheet Wavelength Frequency & Energy Of Electromagnetic Waves
The concepts of wavelength, frequency, and energy are essential in various areas of chemistry, including spectroscopy, photochemistry, and quantum chemistry.
- Spectroscopy: The study of the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. Spectroscopic techniques allow chemists to identify and characterize molecules based on their absorption or emission of specific wavelengths of light.
- Photochemistry: The study of chemical reactions initiated or influenced by the absorption of electromagnetic radiation. Photochemical reactions are used in various applications, such as photography and solar energy conversion.
- Quantum Chemistry: The application of quantum mechanics to understand the behavior of atoms and molecules. Quantum chemistry uses the concepts of wavelength and energy to explain the electronic structure and properties of chemical species.
Clarifying Questions
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional. As wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa.
How does energy relate to wavelength and frequency?
Energy is directly proportional to frequency. Higher frequency electromagnetic waves have higher energy than lower frequency waves.
What are the different types of electromagnetic waves?
The electromagnetic spectrum includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet waves, visible light, infrared waves, microwaves, and radio waves.